
PPT Introduction to Sound PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2795241
When the resonant frequency is reached, the glass shatters. A speaker produces a sound wave by oscillating a cone, causing vibrations of air molecules. In Figure 17.3, a speaker vibrates at a constant frequency and amplitude, producing vibrations in the surrounding air molecules.
Sound velocity, Nature and properties of sound waves Science online
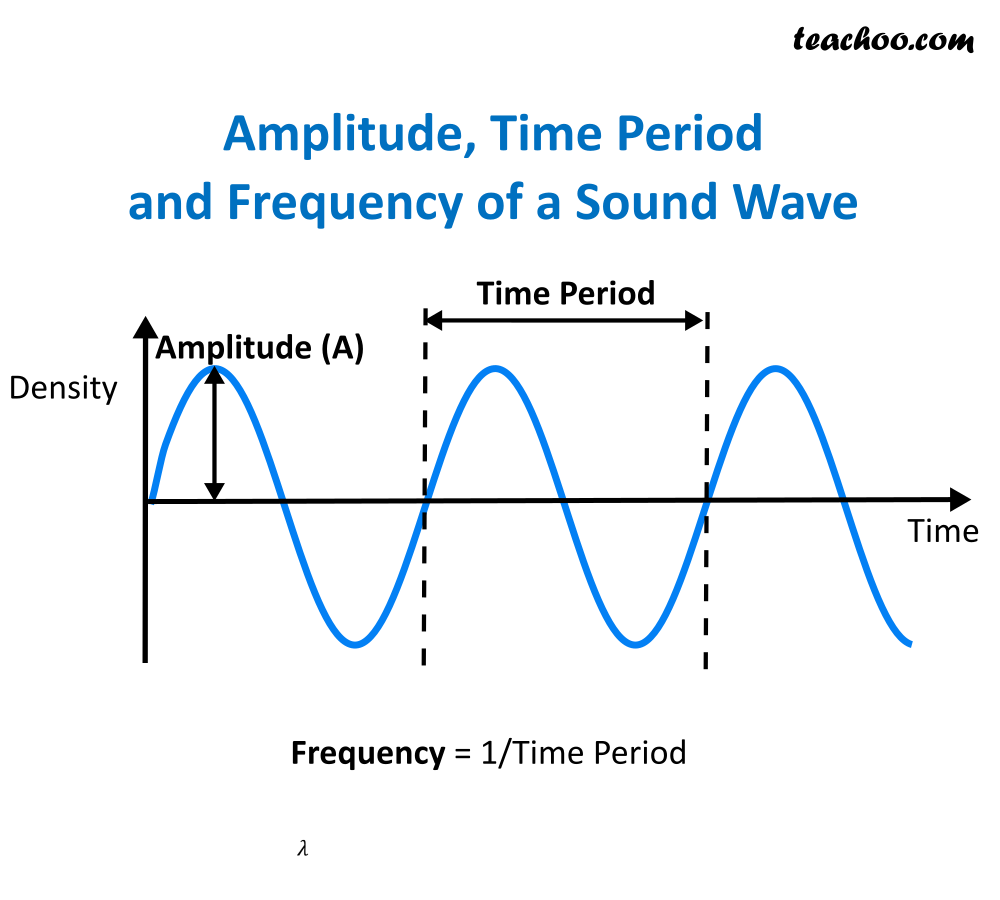
Frequency is defined to be one over the period. So, since the period is the number of seconds per oscillation, the frequency is the number of oscillations per second. Frequency has units of one over seconds, and we call one over a second a hertz. Typical sounds have frequencies in the 100s or even 1000s of hertz.

Watch these sound videos
Lesson 1 - The Nature of a Sound Wave Sound is a Mechanical Wave Sound as a Longitudinal Wave Sound is a Pressure Wave Lesson 2 - Sound Properties and Their Perception Pitch and Frequency Intensity and the Decibel Scale The Speed of Sound The Human Ear Lesson 3 Behavior of Sound Waves Interference and Beats The Doppler Effect and Shock Waves

Amplitude of a sound wave Royalty Free Vector Image
Sound is defined as " (a) Oscillation in pressure, stress, particle displacement, particle velocity, etc., propagated in a medium with internal forces (e.g., elastic or viscous), or the superposition of such propagated oscillation. (b) Auditory sensation evoked by the oscillation described in (a)." [4]

Physics Intro or Basics of Sound Waves YouTube
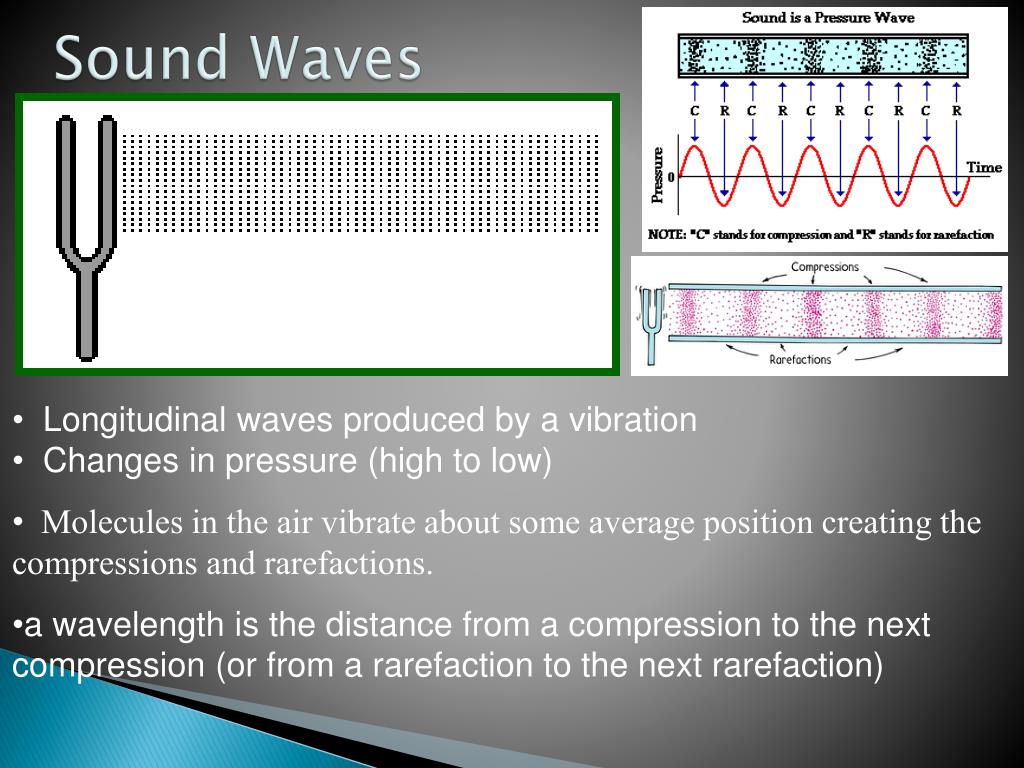
A disturbance is anything that is moved from its state of equilibrium. Some sound waves can be characterized as periodic waves, which means that the atoms that make up the matter experience simple harmonic motion. A vibrating string produces a sound wave as illustrated in Figure 14.2, Figure 14.3, and Figure 14.4.

Sound Waves 1, QLD Edition Super Challenge (Black line masters) Harleys The Educational
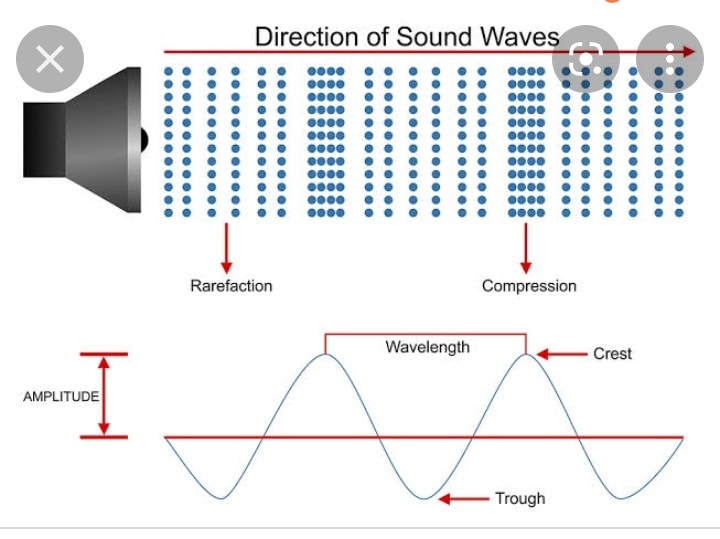
Sound. When a drum is struck, the drumhead vibrates and the vibrations are transmitted through the air in the form of sound waves. When they strike the ear, these waves produce the sensation of sound. Terms used in the study of sound. Acoustics is the science of sound and of its effects on people. Condensation is a region in a sound wave in.

PPT SOUND WAVES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6020601
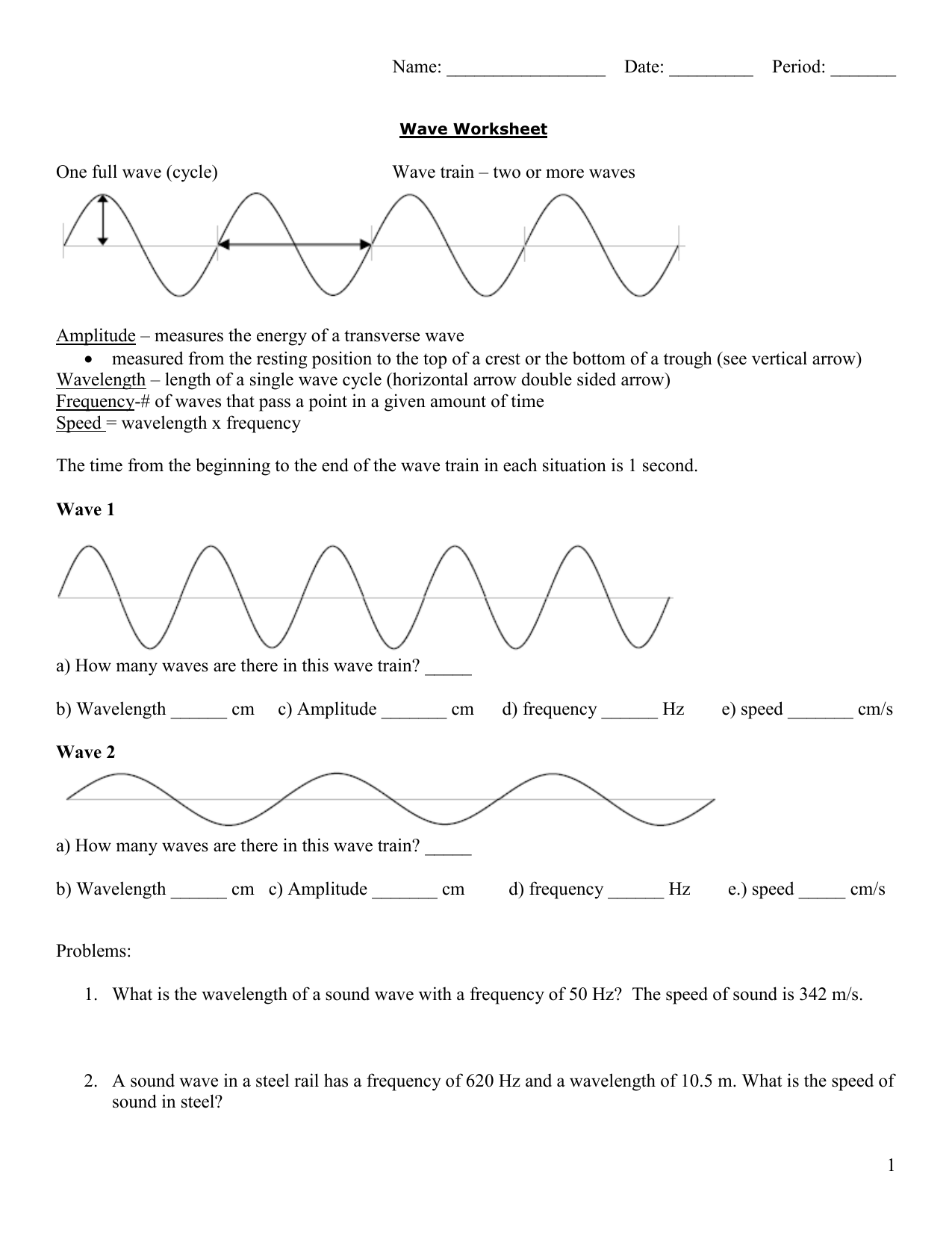
Amplitude Amplitude in light refers to the amount of energy in an electromagnetic wave and its meaning is the same here. Amplitude refers to the distance of the maximum vertical displacement of the wave from its mean position. Larger the amplitude, the higher the energy.
Sound Wave Diagram Labeled
by KOMO News Staff. Wed, January 10th 2024. 6. VIEW ALL PHOTOS. A screengrab from video shows water rushing onto a Washington state ferry during rough seas on Tuesday, January 9, near the Strait.
Unveiling the Secrets of Sound Waves Lesson 1 Understanding the AE Sound Wave Phenomenon
Introduction to waves. Transverse and longitudinal waves are two types of mechanical waves, which involve the transfer of energy through a medium (e.g. water, air, a solid). Learn about transverse and longitudinal waves through the examples of a shaken rope and a sound wave.

Sound Waves Help Particles Heal Research & Development World
In science, sound is defined as the transfer of energy from a vibrating object in waves that travel through matter. All sound waves begin with vibrating matter. The vibrations generate longitudinal waves that travel through matter in all directions. Most sounds we hear travel through air, but sounds can also travel through liquids and solids.
PPT Sound Notes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5906639
Season 1. Sound Waves is a series that captures the intimate moments experienced by the world's best surfers during competition. Each episode hones in on a single surfer's journey at a particular Tour stop, giving the viewer an in-depth look at the Championship Tour and what it takes to be a professional surfer. 9:06.

131 sound waves
General Physics Using Calculus I 17 Sound 17.1 Sound Waves Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the difference between sound and hearing Describe sound as a wave List the equations used to model sound waves Describe compression and rarefactions as they relate to sound
Sound Waves 1
In a transverse wave, such as the wave generated in a stretched rope when one end is wiggled back and forth, the motion that constitutes the wave is perpendicular, or transverse, to the direction (along the rope) in which the wave is moving.
What is Sound and How do we Hear it? Let's Talk Science
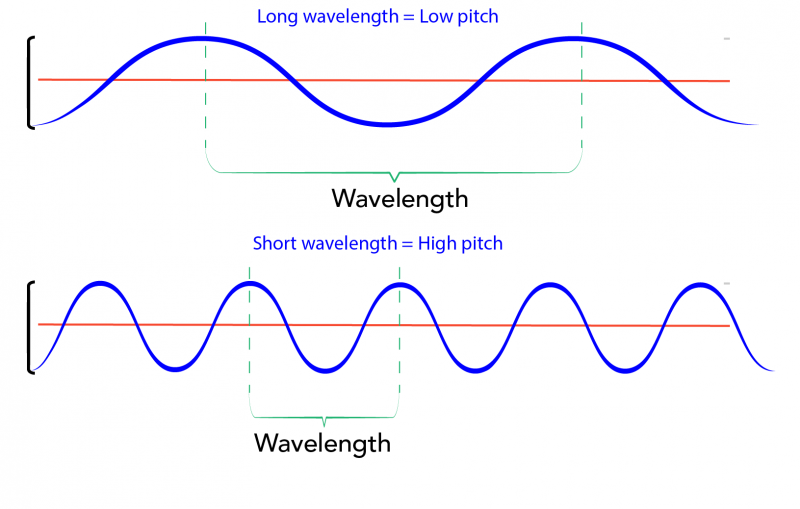
Every five seconds converts to about one mile. The velocity of any wave is related to its frequency and wavelength by v = fλ, v = f λ, 17.3 where v is the speed of the wave, f is its frequency, and λ λ is its wavelength. Recall from Waves that the wavelength is the length of the wave as measured between sequential identical points.

SOUND WAVES 1 WHAT IS SOUND WAVES Sound
PhET Global. DEIB in STEM Ed. Donate. This simulation lets you see sound waves. Adjust the frequency or volume and you can see and hear how the wave changes. Move the listener around and hear what she hears.

Wavelength of Sound Waves Class 9 Science Notes by Teachoo
When the resonant frequency is reached, the glass shatters. A speaker produces a sound wave by oscillating a cone, causing vibrations of air molecules. In (Figure), a speaker vibrates at a constant frequency and amplitude, producing vibrations in the surrounding air molecules.